Your cart is currently empty!
Tag: Cartesian Plane
COORDINATE GEOMETRY | Study
Introduction To Trigonometry | Study
Some Applications Of Trigonometry| Study
COORDINATE GEOMETRY | Study
COORDINATE GEOMETRY | Study

COORDINATE GEOMETRY | Study
Pre-Requisires
Test & Enrich
English Version Coordinate Geometry: Cartesian Plane | Speed Notes
Notes For Quick Recap
Cartesian System

A plane formed by two number lines, one horizontal
and the other vertical, such that they intersect each
other at their zeroes, and then they form a Cartesian
Plane.
Scroll Down To Continue …
Study Tools
Audio, Visual & Digital Content
● The horizontal line is known as the x-axis and the vertical line is known
as the y-axis.
● The point where these two lines intersect each other is called the origin.
It is represented as ‘O’.
● OX and OY are the positive directions as the positive numbers lie in the
right and upward direction.
● Similarly, the left and the downward directions are the negative directions
as all the negative numbers lie there.

Quadrants of the Cartesian Plane The Cartesian plane is divided into four quadrants namely Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, and Quadrant IV anticlockwise from OX.

Coordinates of a Point To write the coordinates of a point we need to follow the following rules. ● Thex – coordinate of a point is marked by drawing perpendicular from the y-axis measured a length of the x-axis .It is also called the Abscissa.

They – coordinate of a point is marked by drawing a perpendicular from the x-axis measured a length of the y-axis .It is also called the Ordinate. ● While writing the coordinates of a point in the coordinate plane, the x – coordinate comes first, and then the y – coordinate. We write the coordinates in brackets. In figure, OB = CA = x coordinate (Abscissa), and CO = AB = y coordinate (Ordinate). We write the coordinate as (x, y).
Remarks:

As the origin, O has zero distance from the x-axis and the y-axis so its abscissa and ordinate are zero. Hence the coordinate of the origin is (0, 0). The relationship between the signs of the coordinates of a point and the quadrant of a point in which it lies.

Plotting a Point in the Plane if its Coordinates are Given

Steps to plot the point (2, 3) on the Cartesian plane:
● First of all, we need to draw the Cartesian plane by drawing the coordinate axes with 1 unit = 1 cm.
● To mark the x coordinates, starting from 0 moves towards the positive x-axis and counts to 2.
● To mark the y coordinate, starting from 2 moves upwards in the positive direction and counts to 3.
● Now this point is the coordinate (2, 3). Likewise, we can plot all the other points, like (-3, 1) and (-1.5,-2.5) in the figure.
Question: Are the coordinates (x, y) = (y, x)? Let x = (-4) and y = (-2) So (x, y) = (- 4, – 2) (y, x) = (- 2, – 4)

Let’s mark these coordinates on the Cartesian plane. You can see that the positions of both the points are different in the Cartesian plane. So, If x ≠ y, then (x, y) ≠ (y, x), and (x, y) = (y, x), if x = y.
Example: Plot the points (6, 4), (- 6,- 4), (- 6, 4) and (6,- 4) on the Cartesian plane.

Solution: Since both numbers 6, 4 are positive the point (6, 4) lies in the first quadrant. For x coordinate, we will move towards the right and count to 6. Then from that point go upward and count to 4. Mark that point as the coordinate (6, 4). Similarly, we can plot all the other three points.
Hindi Version Dig Deep
Topic Level Resources
Sub – Topics
Select A Topic
Topic:
Chapters Index
Select Another Chapter
[display-posts category=”CBSE 9 – Mathematics – Study – Premium” order=”ASC” posts_per_page=”25″]Assessments
Personalised Assessments

Introduction To Trigonometry | Study
Pre-Requisires
Test & Enrich
English Version Introduction To Trigonometry | Speed Notes
Notes For Quick Recap
An angle is positive if its rotation is in the anticlockwise and negative if its rotation is in the clockwise direction.

(Scroll down to continue …)
Study Tools
Audio, Visual & Digital Content


Trigonometric Ratios

If one of the trigonometric ratios of an acute angle is known, the remaining trigonometric ration of the angle can be determined.
Two angles are said to be complementary, if their sum is 900 and each one of them is called the complement of the other.
sin (900 – θ) = Cos θ
Cos (900– θ)= Sin θ
tan (900– θ) = Cot θ
Cot(900– θ) = tan θ
sec (900– θ)= cosec θ
cosec (900– θ) = sec θ
Trigonometric Identities
An equation with trigonometric ratios of an angle θ, which is true for all values of ‘ θ ‘, for which the given trigonometric ratios are defined, is called an identity.
The three fundamental trigonometric identities are

- sin2 θ +cos2 θ = 1
⇒ sin2 θ =1-cos2 θ
⇒ sin2 θ =(1-cos θ)(1+cos θ)
⇒ (1- cos θ) = (sin2 θ) /(1+ cos θ)
⇒ (1+ cos θ) = (sin2 θ) /(1- cos θ)
⇒ cos2 θ + sin2 θ = 1
cos2 θ =1- sin2 θ
⇒ cos2 θ =(1- sin θ)(1+ sin θ)
⇒ (1+ sin θ) = (cos2 θ) /(1- sin θ)
⇒ (1- sin θ) = cos2 θ /(1+sin θ)
(b) sec2 θ = 1 + tan2 θ
⇒ sec2 θ – tan2 θ =1
⇒ (sec θ – tan θ)(sec θ + tan θ) = 1
⇒ (sec θ – tan θ) = 1/ (sec θ + tan θ)
⇒ (sec θ + tan θ) = 1/ (sec θ – tan θ)
⇒ sec2 θ – 1 = tan2 θ
⇒ (sec θ – 1)( sec θ – 1) = tan2 θ
(c) cosec2 θ = 1+cot2θ
⇒ cosec2 θ – cot2 θ = 1
⇒ (cosec θ – cot θ)(cosec θ + cot θ)=1
(cosec θ+ cot θ) =1cosec θ – cot θ
(cosec θ- cot θ) = 1cosec θ + cot θ
⇒ Cosec2 θ – 1 = cot2 θ
⇒ (Cosec θ – 1)( Cosec θ – 1) = Cot2 θ
Supportive Formulae:
(a+b)2=+a2+b2+2ab
(a-b)2 = a2+b2-2ab
(a+b)2+(a-b)2= 2 (a2+b2)
(a+b)2– (a-b)2= 4ab
(a-b)2– (a+b)2= – 4ab
(a+b)2 = (a-b)2+ 4ab
(a-b)2 = (a+b)2– 4ab
(a2-b2)=(a+b)(a-b)
a+b=(a2-b2) /(a-b)
a-b=(a2-b2) /(a-b)
(a+b)2= (a-b)2+ 4ab
Hindi Version Dig Deep
Topic Level Resources
Sub – Topics
Select A Topic
Topic:
Chapters Index
Select Another Chapter
[display-posts category=”CBSE 10 – Mathematics – Study – Premium” posts_per_page=”25″]Assessments
Personalised Assessments
Pre-Requisires
Test & Enrich
English Version Speed Notes
Notes For Quick Recap
Cartesian System

A plane formed by two number lines, one horizontal
and the other vertical, such that they intersect each
other at their zeroes, and then they form a Cartesian
Plane.
Scroll Down To Continue …
Study Tools
Audio, Visual & Digital Content
Coordinate Axes:

The position of a point in a plane is fixed by selecting the axes of reference which are formed by two number lines intersecting each other at right angles, so that their zeroes coincide.
The horizontal number line is called x-axis and vertical number line is called y axis.
A point that lies on X Axis is (x,0)
A point that lies on Y Axis is (0,y)
Equation of Y Axis is x = 0
Equation of X Axis is y = 0
Equation of a lne parallel to Y Axis is x = a
Equation of a lne parallel to X Axis is y = a
Equation of a lne perpendicular to X Axis is X = a
Equation of a lne perpendicular to X Axis is X = a
The point of intersection of the two lines is called origin.

is the x-axis and Y1OY is the y-axis. These coordinate axes are also called rectangular axes as they are perpendicular to each other.
Rectangular coordinates are ordered pairs in which the first element is called the abscissa and the second element is called the ordinate.


● In the first quadrant, x is + ve and y is + ve
● In the second quadrant, x is – ve and y is + ve
● In the third quadrant, x is – ve and y is – ve
● In the fourth quadrant, x is + ve and y is -ve.
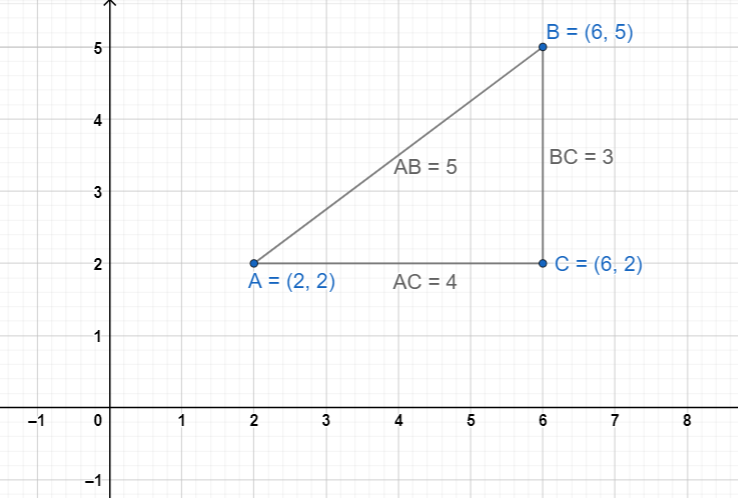
Distance Formula:

Example:

Example:

Collinearity of three points:

Three points P, Q and R are said to be collinear, if they lie in the same straight line.
i.e., PR = PQ + QR
i.e., PQ = PR + RQ
i.e., QR = QP + PR
If three points are not collinear, they always form a triangle.
Special Polygons:
(i) In Case of Triangle
(a) a right-angled triangle, if sum of squares of any two sides is equal to square of third side.
(b) an equilateral triangle, if all the three sides are equal.
(c) an isosceles triangle, if any two sides are equal.
(ii) In Case of Quadrilateral
(a) parallelogram, if opposite sides are equal and diagonals are not equal.
(b) rectangle, if opposite sides are equal and diagonals are equal.
(c) square, if all the four sides are equal and diagonals are equal.
(d) rhombus, if all the four sides are equal and diagonals are not equal.
Section Formula (Internal division only)

Midpoint Formula:

Point Dividing Two points in K : 1 Ratio:

Note:
If k is positive, the point divides the given points internally.
If k is Negative, the point divides the given points externally
Coordinates of the centroid of a triangle:

Points of Trisection:

If a line segment is divided into three equal parts by two points, the points are said to be the points of trisection.
In the given figure, the points R and S divide the line segment PQ into three equal parts i.e., PR=RS=SQ. The points R and S are said to be points of trisection.
Area of a Triangle:
The area of the triangle formed by the points

is calculated by the following expression.
Area of ∆PQR =

Area of Quadrilateral:

Area of a quadrilateral can be found by splitting up the quadrilateral into two triangles and sum up their areas.
Thus, area of quadrilateral PQRS = area of ∆PQR+ area of ∆PRS

Condition for collinearity of three points :
Three given points will be collinear, if the area of the triangle formed by these points is zero.
Rule to prove that three given points are collinear:
Step 1. Find the area of the triangle formed by the given points.
Step 2. Show that the area of the triangle formed by the given points is zero.
* The coordinates of the origin are O(0,0)
* The coordinates of any point on x-axis are (x, 0)
i.e., y=0 or ordinate is zero.
* The coordinates of any point on y – axis are (0, y) i.e., x=0 or abscissa is zero.
Hindi Version Dig Deep
Topic Level Resources
Sub – Topics
Select A Topic
Topic:
Chapters Index
Select Another Chapter
[display-posts category=”CBSE 10 – Mathematics – Study – Premium” order=”ASC” posts_per_page=”25″]Assessments
Personalised Assessments

Some Applications Of Trigonometry| Study
Pre-Requisires
Test & Enrich
English Version Some Applications Of Trigonometry | Speed Notes
Notes For Quick Recap
Introduction :
One of the main applications of trigonometry is to find the distance between two or more than two places or to find the height of the object or the angle subtended by any object at a given point without actually measuring the distance or heights or angles.
Study Tools
Audio, Visual & Digital Content
Trigonometry is useful to astronomers, navigators, architects and surveyors etc. in solving problems related to heights and distances.
The directions of the objects can be described by measuring :
(i) angle of elevation and (ii) angle of depression
Angles of elevation or angles of depression of the objects are measured by an instrument called The odolite.
The odolite is based on the principles of trigonometry, which is used for measuring angles with a rotating telescope.
In 1856, Sir George Everest first used the giant theodolite, which is now on display in the Museum of the survey of India in Dehradun.
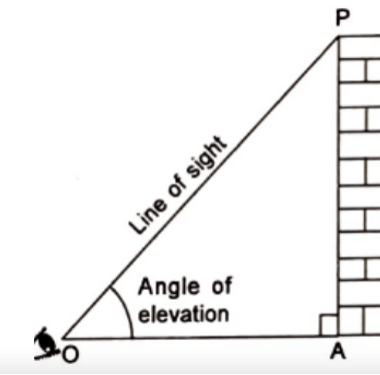
Angle of Elevation:

Let P be the position of the object above the horizontal line OA and O be the eye of the observer, then angle AOP is called angle of elevation. It is called the angle of elevation, because the observer has to elevate (raise) his line of sight from the horizontal OA to see the object P. [ When the eye turns upwards above the horizontal line.]
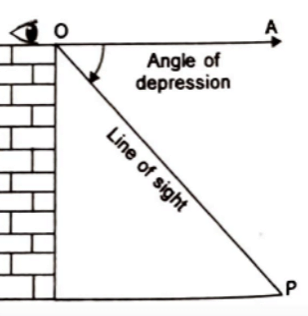
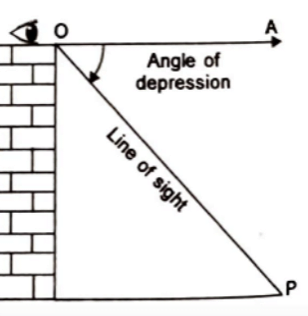
Angle of Depression:

Let P be the position of the object below the horizontal line OA and O be the eye of the observer, then angle AOP is called angle of depression.
It is called the angle of depression because the observer has to depress (lower) his line of sight from the horizontal OA to see the object P.
[When the eye turns downwards below the horizontal line].Hindi Version Dig Deep
Topic Level Resources
Sub – Topics
Select A Topic
Topic:
Chapters Index
Select Another Chapter
[display-posts category=”CBSE 10 – Mathematics – Study – Premium” posts_per_page=”25″]Assessments
Personalised Assessments
Pre-Requisires
Test & Enrich
English Version Speed Notes
Notes For Quick Recap
Cartesian System

A plane formed by two number lines, one horizontal
and the other vertical, such that they intersect each
other at their zeroes, and then they form a Cartesian
Plane.
Scroll Down To Continue …
Study Tools
Audio, Visual & Digital Content
Coordinate Axes:

The position of a point in a plane is fixed by selecting the axes of reference which are formed by two number lines intersecting each other at right angles, so that their zeroes coincide.
The horizontal number line is called x-axis and vertical number line is called y axis.
A point that lies on X Axis is (x,0)
A point that lies on Y Axis is (0,y)
Equation of Y Axis is x = 0
Equation of X Axis is y = 0
Equation of a lne parallel to Y Axis is x = a
Equation of a lne parallel to X Axis is y = a
Equation of a lne perpendicular to X Axis is X = a
Equation of a lne perpendicular to X Axis is X = a
The point of intersection of the two lines is called origin.

is the x-axis and Y1OY is the y-axis. These coordinate axes are also called rectangular axes as they are perpendicular to each other.
Rectangular coordinates are ordered pairs in which the first element is called the abscissa and the second element is called the ordinate.


● In the first quadrant, x is + ve and y is + ve
● In the second quadrant, x is – ve and y is + ve
● In the third quadrant, x is – ve and y is – ve
● In the fourth quadrant, x is + ve and y is -ve.
Distance Formula:

Example:

Example:

Collinearity of three points:

Three points P, Q and R are said to be collinear, if they lie in the same straight line.
i.e., PR = PQ + QR
i.e., PQ = PR + RQ
i.e., QR = QP + PR
If three points are not collinear, they always form a triangle.
Special Polygons:
(i) In Case of Triangle
(a) a right-angled triangle, if sum of squares of any two sides is equal to square of third side.
(b) an equilateral triangle, if all the three sides are equal.
(c) an isosceles triangle, if any two sides are equal.
(ii) In Case of Quadrilateral
(a) parallelogram, if opposite sides are equal and diagonals are not equal.
(b) rectangle, if opposite sides are equal and diagonals are equal.
(c) square, if all the four sides are equal and diagonals are equal.
(d) rhombus, if all the four sides are equal and diagonals are not equal.
Section Formula (Internal division only)

Midpoint Formula:

Point Dividing Two points in K : 1 Ratio:

Note:
If k is positive, the point divides the given points internally.
If k is Negative, the point divides the given points externally
Coordinates of the centroid of a triangle:

Points of Trisection:

If a line segment is divided into three equal parts by two points, the points are said to be the points of trisection.
In the given figure, the points R and S divide the line segment PQ into three equal parts i.e., PR=RS=SQ. The points R and S are said to be points of trisection.
Area of a Triangle:
The area of the triangle formed by the points

is calculated by the following expression.
Area of ∆PQR =

Area of Quadrilateral:

Area of a quadrilateral can be found by splitting up the quadrilateral into two triangles and sum up their areas.
Thus, area of quadrilateral PQRS = area of ∆PQR+ area of ∆PRS

Condition for collinearity of three points :
Three given points will be collinear, if the area of the triangle formed by these points is zero.
Rule to prove that three given points are collinear:
Step 1. Find the area of the triangle formed by the given points.
Step 2. Show that the area of the triangle formed by the given points is zero.
* The coordinates of the origin are O(0,0)
* The coordinates of any point on x-axis are (x, 0)
i.e., y=0 or ordinate is zero.
* The coordinates of any point on y – axis are (0, y) i.e., x=0 or abscissa is zero.
Hindi Version Dig Deep
Topic Level Resources
Sub – Topics
Select A Topic
Topic:
Chapters Index
Select Another Chapter
[display-posts category=”CBSE 10 – Mathematics – Study – Premium” order=”ASC” posts_per_page=”25″]Assessments
Personalised Assessments

COORDINATE GEOMETRY | Study
Pre-Requisires
Test & Enrich
English Version Speed Notes
Notes For Quick Recap
Cartesian System

A plane formed by two number lines, one horizontal
and the other vertical, such that they intersect each
other at their zeroes, and then they form a Cartesian
Plane.
Scroll Down To Continue …
Study Tools
Audio, Visual & Digital Content
Coordinate Axes:

The position of a point in a plane is fixed by selecting the axes of reference which are formed by two number lines intersecting each other at right angles, so that their zeroes coincide.
The horizontal number line is called x-axis and vertical number line is called y axis.
A point that lies on X Axis is (x,0)
A point that lies on Y Axis is (0,y)
Equation of Y Axis is x = 0
Equation of X Axis is y = 0
Equation of a lne parallel to Y Axis is x = a
Equation of a lne parallel to X Axis is y = a
Equation of a lne perpendicular to X Axis is X = a
Equation of a lne perpendicular to X Axis is X = a
The point of intersection of the two lines is called origin.

is the x-axis and Y1OY is the y-axis. These coordinate axes are also called rectangular axes as they are perpendicular to each other.
Rectangular coordinates are ordered pairs in which the first element is called the abscissa and the second element is called the ordinate.


● In the first quadrant, x is + ve and y is + ve
● In the second quadrant, x is – ve and y is + ve
● In the third quadrant, x is – ve and y is – ve
● In the fourth quadrant, x is + ve and y is -ve.
Distance Formula:

Example:

Example:

Collinearity of three points:

Three points P, Q and R are said to be collinear, if they lie in the same straight line.
i.e., PR = PQ + QR
i.e., PQ = PR + RQ
i.e., QR = QP + PR
If three points are not collinear, they always form a triangle.
Special Polygons:
(i) In Case of Triangle
(a) a right-angled triangle, if sum of squares of any two sides is equal to square of third side.
(b) an equilateral triangle, if all the three sides are equal.
(c) an isosceles triangle, if any two sides are equal.
(ii) In Case of Quadrilateral
(a) parallelogram, if opposite sides are equal and diagonals are not equal.
(b) rectangle, if opposite sides are equal and diagonals are equal.
(c) square, if all the four sides are equal and diagonals are equal.
(d) rhombus, if all the four sides are equal and diagonals are not equal.
Section Formula (Internal division only)

Midpoint Formula:

Point Dividing Two points in K : 1 Ratio:

Note:
If k is positive, the point divides the given points internally.
If k is Negative, the point divides the given points externally
Coordinates of the centroid of a triangle:

Points of Trisection:

If a line segment is divided into three equal parts by two points, the points are said to be the points of trisection.
In the given figure, the points R and S divide the line segment PQ into three equal parts i.e., PR=RS=SQ. The points R and S are said to be points of trisection.
Area of a Triangle:
The area of the triangle formed by the points

is calculated by the following expression.
Area of ∆PQR =

Area of Quadrilateral:

Area of a quadrilateral can be found by splitting up the quadrilateral into two triangles and sum up their areas.
Thus, area of quadrilateral PQRS = area of ∆PQR+ area of ∆PRS

Condition for collinearity of three points :
Three given points will be collinear, if the area of the triangle formed by these points is zero.
Rule to prove that three given points are collinear:
Step 1. Find the area of the triangle formed by the given points.
Step 2. Show that the area of the triangle formed by the given points is zero.
* The coordinates of the origin are O(0,0)
* The coordinates of any point on x-axis are (x, 0)
i.e., y=0 or ordinate is zero.
* The coordinates of any point on y – axis are (0, y) i.e., x=0 or abscissa is zero.
Hindi Version Dig Deep
Topic Level Resources
Sub – Topics
Select A Topic
Topic:
Chapters Index
Select Another Chapter
[display-posts category=”CBSE 10 – Mathematics – Study – Premium” order=”ASC” posts_per_page=”25″]
COORDINATE GEOMETRY | Study
Pre-Requisires
Test & Enrich
English Version Coordinate Geometry: Cartesian Plane | Speed Notes
Notes For Quick Recap
Cartesian System

A plane formed by two number lines, one horizontal
and the other vertical, such that they intersect each
other at their zeroes, and then they form a Cartesian
Plane.
Scroll Down To Continue …
Study Tools
Audio, Visual & Digital Content
● The horizontal line is known as the x-axis and the vertical line is known
as the y-axis.
● The point where these two lines intersect each other is called the origin.
It is represented as ‘O’.
● OX and OY are the positive directions as the positive numbers lie in the
right and upward direction.
● Similarly, the left and the downward directions are the negative directions
as all the negative numbers lie there.

Quadrants of the Cartesian Plane The Cartesian plane is divided into four quadrants namely Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, and Quadrant IV anticlockwise from OX.

Coordinates of a Point To write the coordinates of a point we need to follow the following rules. ● Thex – coordinate of a point is marked by drawing perpendicular from the y-axis measured a length of the x-axis .It is also called the Abscissa.

They – coordinate of a point is marked by drawing a perpendicular from the x-axis measured a length of the y-axis .It is also called the Ordinate. ● While writing the coordinates of a point in the coordinate plane, the x – coordinate comes first, and then the y – coordinate. We write the coordinates in brackets. In figure, OB = CA = x coordinate (Abscissa), and CO = AB = y coordinate (Ordinate). We write the coordinate as (x, y).
Remarks:

As the origin, O has zero distance from the x-axis and the y-axis so its abscissa and ordinate are zero. Hence the coordinate of the origin is (0, 0). The relationship between the signs of the coordinates of a point and the quadrant of a point in which it lies.

Plotting a Point in the Plane if its Coordinates are Given

Steps to plot the point (2, 3) on the Cartesian plane:
● First of all, we need to draw the Cartesian plane by drawing the coordinate axes with 1 unit = 1 cm.
● To mark the x coordinates, starting from 0 moves towards the positive x-axis and counts to 2.
● To mark the y coordinate, starting from 2 moves upwards in the positive direction and counts to 3.
● Now this point is the coordinate (2, 3). Likewise, we can plot all the other points, like (-3, 1) and (-1.5,-2.5) in the figure.
Question: Are the coordinates (x, y) = (y, x)? Let x = (-4) and y = (-2) So (x, y) = (- 4, – 2) (y, x) = (- 2, – 4)

Let’s mark these coordinates on the Cartesian plane. You can see that the positions of both the points are different in the Cartesian plane. So, If x ≠ y, then (x, y) ≠ (y, x), and (x, y) = (y, x), if x = y.
Example: Plot the points (6, 4), (- 6,- 4), (- 6, 4) and (6,- 4) on the Cartesian plane.

Solution: Since both numbers 6, 4 are positive the point (6, 4) lies in the first quadrant. For x coordinate, we will move towards the right and count to 6. Then from that point go upward and count to 4. Mark that point as the coordinate (6, 4). Similarly, we can plot all the other three points.
Hindi Version Dig Deep
Topic Level Resources
Sub – Topics
Select A Topic
Topic:
Chapters Index
Select Another Chapter
[display-posts category=”CBSE 9 – Mathematics – Study – Premium” order=”ASC” posts_per_page=”25″]Assessments
Personalised Assessments