Pre-Requisires
Test & Enrich
Understanding Elementary Shapes |Speed Notes
Notes For Quick Recap
The distance betweenthe end pointsof a line segment is its length. A graduatedruler and the divider are useful to compare lengthsof line segments. When a hand of a clock moves from one position to another position we have an examplefor an angle. (Scroll down to continue …)
Study Tools
Audio, Visual & Digital Content
One full turn of the hand is 1 revolution.
A right angle is ¼ revolution and a straight angle is ½ a revolution. We use a protractor to measure the size of an angle in degrees.
The measure of a right angle is 90° and hence that of a straight angle is 180°.
An angle is acute if its measure is smaller than that of a right angle and is obtuseif its measure is greaterthan that of a right angle and less than a straightangle.
A reflex angle is largerthan a straight angle.
Two intersecting lines are perpendicular if the anglebetween them is 90°.
The perpendicular bisector of a line segmentis a perpendicular to the line segmentthat divides it into two equal parts.
Triangles can be classified as follows based on their angles:
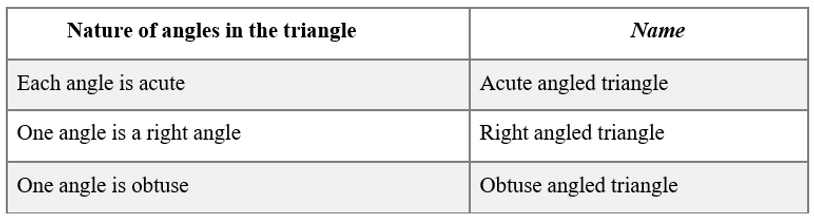
Triangles can be classified as follows based on the lengths of their sides:
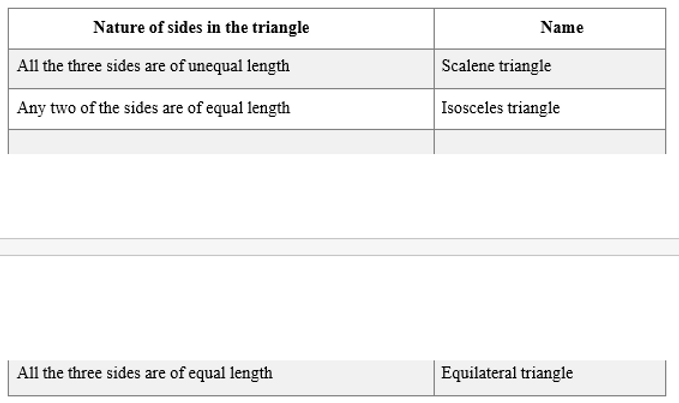
Polygons are namedbased on theirsides.
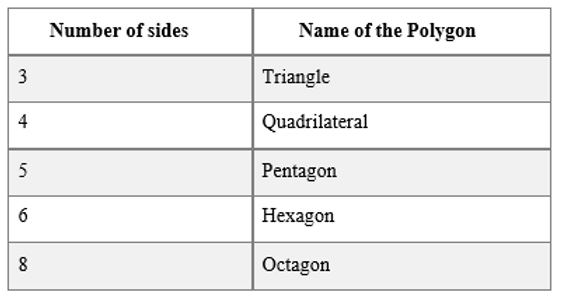
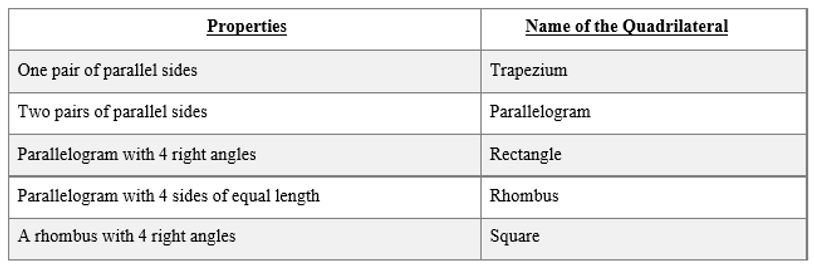
Quadrilaterals are furtherclassified with reference to their properties.
Quadrilateral
Quadrilateral is a closed figure with four sides.
Characteristics of a quadrilateral
Angle Sum Property of a Quadrilateral:
Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
Types Of Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals are broadly classified into two categories as:
(i) Trapezium
(ii) Kite
Trapezium:
Trapezium is a quadrilateral with the following characteristics:
(i) One pair of opposite sides is parallel to each other.
(ii) The other pair of opposite sides may not be parallel to each other.
Characteristics Of Trapezium
(i) Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
(ii) One pair of opposite sides is parallel to each other.
(iii) The other pair of opposite sides need not be parallel to each other.
Types Of Trapezium:
Quadrilaterals are broadly classified into two categories as:
(i) Isosceles Trapezium.
(ii) Scalene Trapezium.
(i) Right Trapezium.
Isosceles Trapezium:
Isosceles Trapezium is a quadrilateral with the following characteristics:
(i) One pair of opposite sides is parallel to each other.
(ii) The other pair of opposite sides are equal.
(iii) The other pair of opposite sides need not be parallel to each other.
Isosceles Trapezium is a trapezium with the following characteristics:
(i) One pair of opposite sides is parallel to each other.
(ii) The other pair of opposite sides are equal.
(iii) The other pair of opposite sides need not be parallel to each other.
Characteristics Of Isosceles Trapezium
(i) Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
(ii) One pair of opposite sides is parallel to each other.
(iii) The other pair of opposite sides are equal.
(iv) The other pair of opposite sides need not be parallel to each other.
Scalene Trapezium:
- Scalene trapezium: Classified by the length of the legs or the measurement of their angles.
Characteristics Of Scalene Trapezium
Right Trapezium:
- Right trapezium: Has one pair of parallel sides and one pair of right angles.
Characteristics Of Right Trapezium
Perimeter Of Trapezium
Area Of Trapezium
Parallelogram:
Parallelogram is a quadrilateral with the following characteristics:
(i) Two pairs of opposite sides are parallel to each other.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite sides are equal in length.
Characteristics of a parallelogram
(i) Sum of all angles of a Parallelogram is 360°.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite sides are parallel to each other.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite sides are equal in length.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite angles are equal.
(iii) Diagonals bisect each other.
(iv) Diagonals need not be equal to each other.
(v) Diagonals divide it into two congruent triangles.
Types Of Parallelogram
Parallelograms are broadly classified into three categories as:
(i) Rectangle
(ii) Rhombus
(iii) Square
Perimeter Of Parallelogram
Area Of Parallelogram
Rectangle:
Rectangle is a quadrilateral with the following characteristics:
(i) Two pairs of opposite sides are parallel to each other.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite sides are equal in length.
(iii) All four angles are right angles. (each angle is 90 o).
Characteristics Of Rectangle
(i) Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite sides are parallel to each other.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite sides are equal in length.
(iii) All four angles are right angles. (each angle is 90 o).
(iii) Diagonals bisect each other.
(iv) Diagonals are equal to each other.
(v) Diagonals of a rectangle divide it into two congruent triangles.
Conclusions:
- Every Rectangle is a Parallelogram. But Every Parallelogram need not to be a Rectangle.
Condition for a rhombus to be a square:
If all four angles of a parallelogram are right angles. (each angle is 90 o), the parallelogram becomes a Rectangle.
Perimeter Of Rectangle
Area Of Recatangle
Rhombus:
Rhombus is a quadrilateral with the following characteristics:
(i) Two pairs of opposite sides are parallel to each other.
(ii) All four sides are equal in length.
Characteristics Of Rhombus
(i) Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite sides are parallel to each other.
(ii) All four sides are equal in length.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite angles are equal.
(iii) Diagonals bisect each other.
(iv) Diagonals need not be equal to each other.
(v) Diagonals divide a Rhombus into two congruent triangles.
Conclusions:
- Every Rhombus is a Parallelogram. But Every Parallelogram need not to be a Rhombus.
Condition for a rhombus to be a square:
If all the sides of a parallelogram are equal, the parallelogram becomes a Rhombus.
Perimeter Of Rhombus
Area Of Rhombus
Square:
Square is a quadrilateral with the following characteristics:
(i) Two pairs of opposite sides are parallel to each other.
(ii) All four sides are equal in length.
(iii) All four angles are right angles. (each angle is 90 o).
Characteristics Of Square
(i) Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
(ii) Two pairs of opposite sides are parallel to each other.
(iii) All four sides are equal in length.
(iv) All four angles are right angles. (each angle is 90 o).
(v) Diagonals bisect each other.
(vi) Diagonals need not be equal to each other.
(vii) Diagonals divide a Rhombus into two congruent triangles.
Conclusions:
- Every square is a Rhombus. But Every Rhombus need not to be a square.
Condition for a rhombus to be a square:
If all the angles of a rhombus are right angles (euqal to 90o), the rhombus becomes a square.
2. Every Square is a prallelogram. But Every prallelogram need not to be a square.
Condition for a prallelogram to be a square:
(i) If all the angles of a parallelogram are right angles (euqal to 90o), and all the sides of a parallelogram are equal in length, the parallelogram becomes a square.
3. Every Square is a rectangle. But Every Rectangle need not to be a square.
Condition for a Rectangle to be a square:
If all the sides of a Rectangle are equal in length, the Rectangle becomes a square.
If all the sides of a parallelogram are equal, the parallelogram becomes a Rhombus.
Perimeter Of Square
Area Of Square
Kite:
(i) Kite has a pair of equal adjacent sides.
(ii) It is not a parallelogram
Characteristics Of Kite:
Perimeter Of Square
Area Of Kite
Important Points To Remember
- The diagonals of a parallelogram are equal if and only if it is a rectangle.
- If a diagonal of a parallelogram bisects one of the angles of the parallelogram then it also bisects the opposite angle.
- In a parallelogram, the bisectors of any two consecutive angles intersect at a right angle.
- The angle bisectors of a parallelogram form a rectangle.
Mid Point Theorem
A line segment joining the mid points of any two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and length of the line segment is half of the parallel side.
Converse Of Mid Point Theorem
A line through the midpoint of a side of a triangle parallel to another side bisects the third side.
Intercept Theorem
If there are three parallel lines and the intercepts made by them on one transversal are equal then the intercepts on any other transversal are also equal.
·We see aroundus many three dimensional shapes.Cubes, cuboids, spheres,
cylinders, cones,prisms and pyramidsare some of them.
Dig Deep
Topic Level Resources
Sub – Topics
Select A Topic
Topic:
Chapters Index
Select Another Chapter
[display-posts category=”CBSE 6 – Mathematics – Study – Premium” posts_per_page=”25″]
Assessments
Personalised Assessments




